Introduction
Bone cancer is a rare but serious condition that can affect individuals of all ages. While it represents a small fraction of all cancer cases, understanding its causes, recognizing its symptoms, and knowing the available treatment options are crucial for early detection and improved outcomes. In this article, we will explore bone cancer, its risk factors, common symptoms, and the various treatment approaches available to patients.
What is Bone Cancer?

Bone cancer, as the name suggests, originates in the bones of the body. It occurs when abnormal cells within the bone tissue begin to multiply uncontrollably, forming a tumor. These tumors can be benign (non-cancerous) or malignant (cancerous). Malignant bone tumors are what we refer to as bone cancer.
Types of Bone Cancer
There are several types of bone cancer, but the most common ones include:
- Osteosarcoma: This form of bone cancer often occurs in the long bones, such as the arms and legs. It typically affects adolescents and young adults.
- Chondrosarcoma: Chondrosarcoma develops in the cartilage, primarily in the pelvis, thigh bone, or shoulder. It is more common in older adults.
- Ewing Sarcoma: Ewing sarcoma usually affects the bones and soft tissues of the pelvis, legs, and arms. It primarily occurs in children and young adults.
Causes and Risk Factors
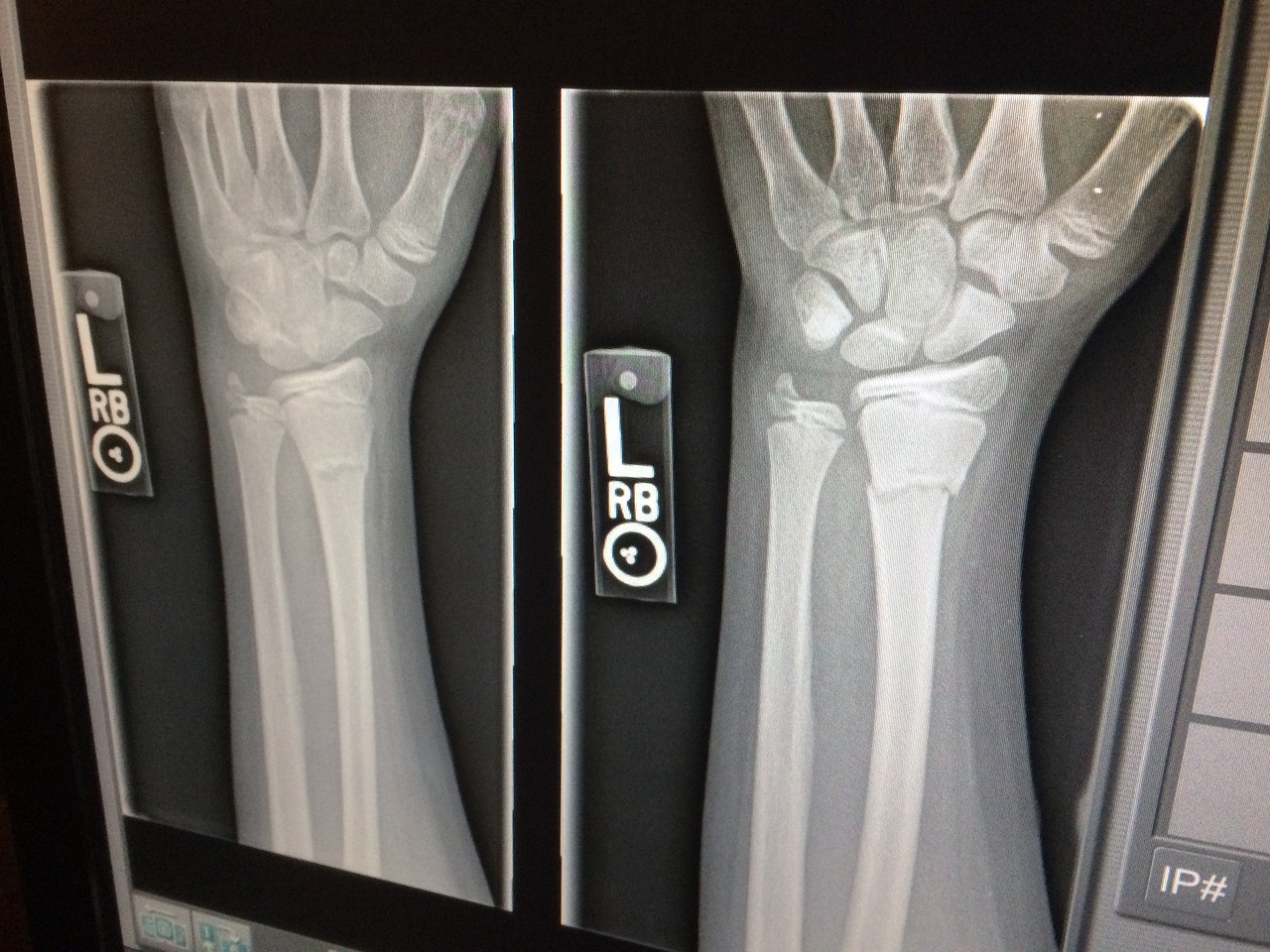
The exact cause of bone cancer remains unclear, but several risk factors may increase a person’s likelihood of developing it:
- Genetic Factors: Some genetic conditions, such as Li-Fraumeni syndrome and hereditary retinoblastoma, can predispose individuals to bone cancer.
- Radiation Exposure: High doses of radiation therapy, often used to treat other cancers, can increase the risk of bone cancer in the treated area.
- Paget’s Disease: This chronic bone disorder can sometimes lead to the development of bone cancer.
- Family History: Having a family member with bone cancer may slightly elevate the risk.
Common Symptoms

Early detection of bone cancer is crucial for effective treatment. However, the symptoms can be subtle and may mimic other, less severe conditions. Common signs and symptoms of bone cancer include:
- Bone Pain: Persistent, deep, and often worsening bone pain, which may be worse at night or during physical activity.
- Swelling and Tenderness: Swelling around the affected area, accompanied by tenderness and warmth.
- Unexplained Weight Loss: Significant and unexplained weight loss without changes in diet or exercise.
- Fatigue: Generalized weakness and fatigue that does not improve with rest.
- Fractures: Bones weakened by the tumor may break (fracture) more easily.
Treatment Options
The choice of treatment for bone cancer depends on several factors, including the type of bone cancer, the stage of the disease, and the patient’s overall health. Treatment options may include:
- Surgery: Surgical removal of the cancerous tumor is a common treatment for bone cancer. In some cases, this may involve limb-sparing surgery to remove the tumor while preserving the affected limb’s function. In more severe cases, amputation may be necessary.
- Radiation Therapy: High-energy X-rays are used to target and destroy cancer cells. Radiation therapy is often used in combination with surgery to ensure the removal of any remaining cancer cells.
- Chemotherapy: Powerful drugs are administered to kill cancer cells or prevent their growth. Chemotherapy is typically used when the cancer has spread beyond the bone or when surgery is not an option.
- Targeted Therapy: Some bone cancers respond to targeted therapies that specifically target cancer cells and spare healthy tissue.
- Clinical Trials: Participation in clinical trials may be an option for some patients, offering access to innovative treatments that are still under investigation.
- Palliative Care: For individuals with advanced bone cancer, palliative care focuses on managing pain, improving quality of life, and providing emotional support.
Conclusion
Bone cancer is a challenging diagnosis, but with early detection and appropriate treatment, the prognosis can be improved. If you or someone you know experiences persistent bone pain, swelling, or any of the symptoms mentioned, it is essential to consult a healthcare professional promptly. Regular check-ups, a healthy lifestyle, and awareness of risk factors can also contribute to the prevention and early detection of bone cancer.
Remember, each case of bone cancer is unique, and treatment plans should be tailored to the individual’s specific circumstances. With advancements in medical technology and research, the outlook for bone cancer patients continues to improve, offering hope and better chances for a full recovery.






